Study: Better understanding is key to beating diabetes
In a presentation at the EURETINA 2021 Virtual Conference, Tunde Peto, MD, PhD, pointed out that while complications associated with diabetes develop over a long period, ophthalmologists today have an excellent understanding of diabetes-related eye changes.
This article was reviewed by Tunde Peto, MD, PhD
Physicians and health systems are challenged to provide appropriate care for the ever-increasing number of patients with diabetes and its complications, such as diabetic retinopathy (DR) and diabetic macular edema (DME).
According to Tunde Peto, MD, PhD, a professor of clinical ophthalmology at Queen’s University Belfast in Belfast, Northern Ireland, and clinical lead for Diabetic Eye Screening in Northern Ireland and a medical retina consultant, offered some practical advice to address some of these challenges during a presentation at the EURETINA 2021 Virtual Congress.
The Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) Barometer Study1 analyzed data from more than 4000 patients and 2000 doctors worldwide showing just how difficult living with and managing diabetes can be.
The study results showed that almost 40% of patients describe the long wait times for an appointment as a barrier to eye examinations.
About 80% of respondents said that diabetes and DR and DME impacted their ability to function in daily life, making driving, working, and completing the most basic household tasks difficult to impossible.
Twenty percent reported that their visual impairment resulting from DR and DME made managing diabetes difficult; and 69% described days during which they experienced poor physical/mental health.
These difficulties in some settings might be compounded by the fact that 1 in 5 ophthalmologists said that they did not receive specific training in diagnosing DR and DME, and 44% of care providers did not have or use written protocols for managing diabetic eye disease and related visual loss.
Dual problem-solving approach
Peto said she believes education, timely diagnosis, and treatment are the key components for preventing visual loss and preserving vision.
Working together with patients and patient organization and co-developing education material will raise awareness of the disease.
Diabetic eye screening programs can significantly address the problems associated with late diagnosis of DR and DME leading to timely treatment and consequently better quality of life.
Complications associated with diabetes develop over a long period and regular monitoring can identify most patients at a stage in which treatment is most beneficial. DR and DME lend themselves to image-based monitoring.
Physicians have an excellent understanding of diabetes-related eye changes, starting with the Airlie House Classification of DR.2
Landmark studies such as the Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study and the Diabetes Control and Complications Trial established a good understanding of the disease process.3,4
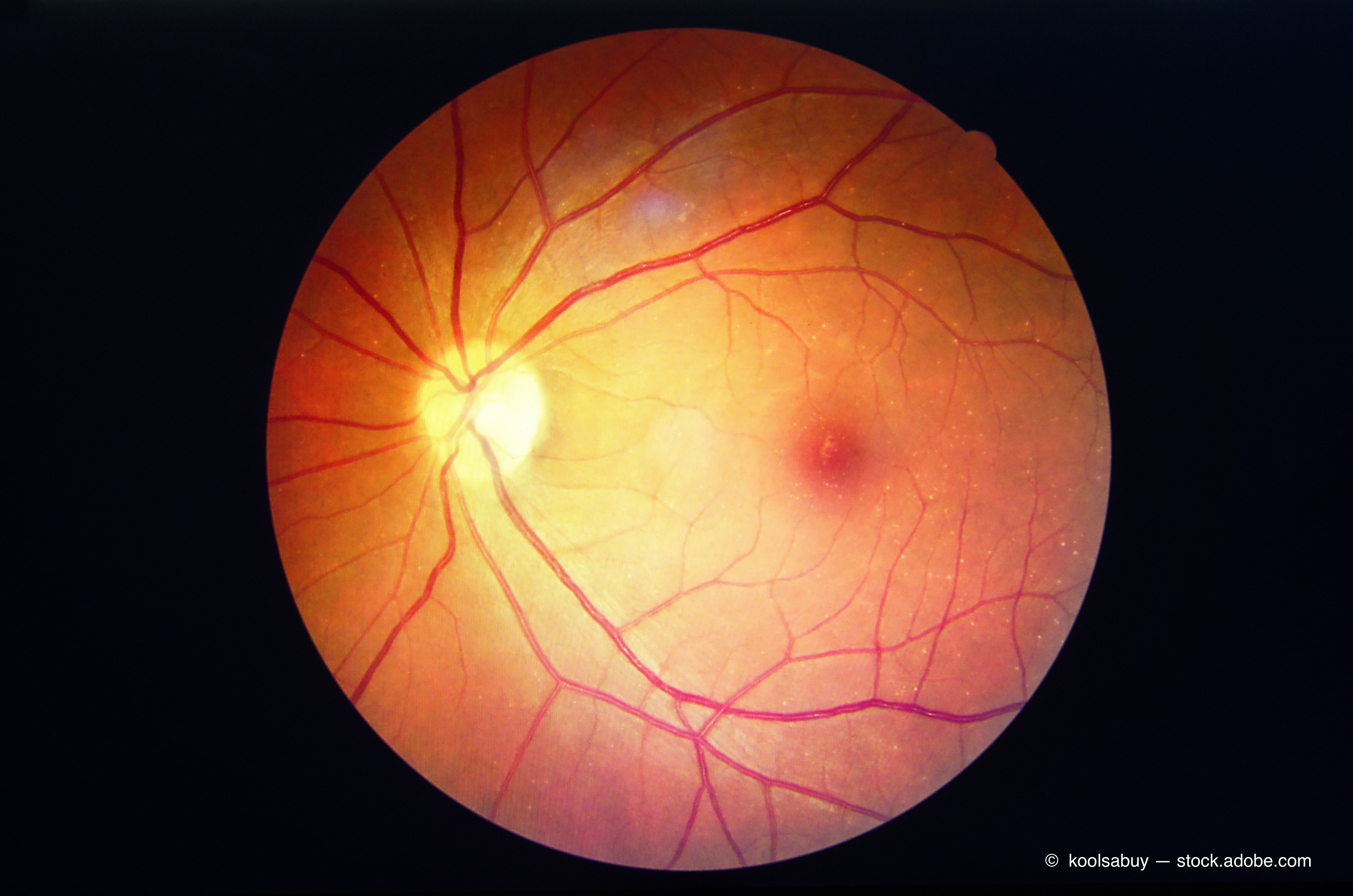
DR classification has been based on the presence of characteristic features in the eye or color fundus imaging of microaneurysms, hemorrhages, vascular abnormalities, and new vessels, and for DME on these changes and exudates and macular fluid.
“With advances in imaging technologies, we now have the opportunity to refine these and add further disease features to match our current understanding of the disease, its progression, and the potential response to treatment,” Peto concluded. “Diabetes-related blindness still increases by 8% annually, so working with patients, care givers, public health agencies, and the healthcare sector, our patients with diabetes will have a better chance of retaining their vision and live a productive life.”
---
References
1. Cavan D, Makaroff L, da Rocha Fernandes J, et al. The Diabetic Retinopathy Barometer Study: Global perspectives on access to and experiences of diabetic retinopathy screening and treatment. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 2017;129:16-24; DOI: 10.1016/j.diabres.2017.03.023
2. Wu L, Fernandez-Loaiza P, Sauma J, et al. Classification of diabetic retinopathy and diabetic macular edema. World J Diabetes 2013;4:290-4; doi: 10.4239/wjd.v4.i6.290
3. Early Treatment Diabetic Retinopathy Study Research Group. Grading diabetic retinopathy from stereoscopic color fundus photographs--an extension of the modified Airlie House classification. ETDRS report number 10. Ophthalmology 1991;98:786–806.
4. Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group; Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med 1993;329:977-86; doi: 10.1056/NEJM199309303291401
Newsletter
Keep your retina practice on the forefront—subscribe for expert analysis and emerging trends in retinal disease management.